Quinoa is a superfood packed with nutrients. It has gained popularity among health-conscious individuals and sustainable farming enthusiasts. Especially among young people. This healthy grain is increasingly being embraced due to its nutritional value and ease of Quinoa Cultivation. In this expansive blog, we shall learn about Quinoa Cultivation by providing in-depth expertise and pragmatic counsel to those keen on cultivating crops. Let’s start with Guide of Plants.
Know More: Crop Farming
Table of Contents
What is Quinoa?

Hailing from the Andean territory of South America, quinoa (articulated keen-way) is a cereal harvest revered for its remarkable wholesome characteristics. With its fragile harmony of protein, fiber, nutrients, and minerals, quinoa has garnered the appellation of a superfood. Diverse types of quinoa cultivation are obtainable, encompassing white, red, and black, each with distinctive flavor and consistency.
Know More: Chak Hao Rice (The Black Rice)
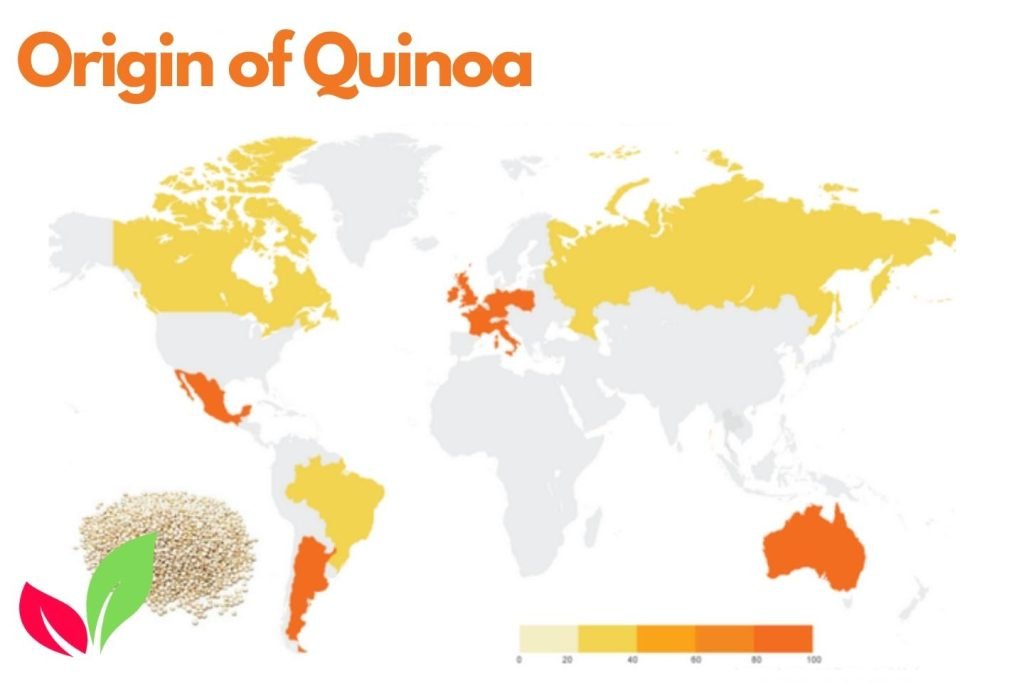
Origin of Quinoa
Quinoa has been grown in South America for centuries by indigenous peoples. It was a staple crop for ancient civilizations such as the Incas. The extreme atmospheric circumstances of the Andes’ elevated areas render them the perfect place for quinoa, recognized for its versatility. Today, quinoa is known for its nutritional value and is cultivated globally. However, quinoa cultivation is still primarily grown in the Andean countries.
Quinoa Seeds
Quinoa seeds are tasty and healthy. They come in different colors and are full of nutrients. You need to cook them to eat them. They are good in lots of other foods like salads and soups. They are also gluten-free, which is fantastic if you cannot consume gluten. Peoples from across the globe are fond of consuming quinoa seeds due to their numerous health benefits and versatility in preparation.
Is Quinoa Gluten-free
Quinoa is excellent cause it doesn’t have gluten, which can cause tummy troubles for some folks. Moreover, it incorporates a profusion of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It has attained tremendous fame and is incorporated into various dishes like pasta, salads, and baked goods. Get certified gluten-free quinoa or from a place that’s careful about cross-contamination. Quinoa is a fantastic alternative for individuals who cannot tolerate gluten or are interested in a nutritious substitute for traditional grains.
Types of Quinoa
Several types of quinoa are available, each with unique color, flavor, and texture characteristics. Here are some of the most common types of quinoa:

White Quinoa: White quinoa is the most widely available and commonly consumed variety. It has a mild flavor and a fluffy texture when cooked. White quinoa is versatile and can be used in a variety of dishes.
Red Quinoa: Red quinoa has a slightly nuttier and earthier flavor than white quinoa. It retains its shape and texture better after cooking, making it suitable for salads, pilafs, and side dishes. Red quinoa adds vibrant color to dishes and is famous for its visual appeal.
Black Quinoa: Black quinoa has a slightly sweeter and earthier flavor than white quinoa. It has a firmer texture and retains its shape well when cooked, making it suitable for grain bowls, stuffing, and hearty salads. Black quinoa also offers a visually striking element to dishes.
Tri-Color Quinoa: Tri-color quinoa blends white, red, and black quinoa. It offers a combination of flavors and textures from the different varieties. Tri-color quinoa is visually appealing and adds variety to recipes, making it a popular choice for salads, side dishes, and main courses.
It’s important to note that while there are variations in taste and texture among these quinoa types, their nutritional profiles are relatively similar. All varieties of quinoa are high in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them nutritious additions to a balanced diet.
Growing Conditions and Climate Requirements
Quinoa flourishes under particular environmental conditions. Thus, it is crucial to comprehend its favored growing circumstances. This cereal crop thrives in mild temperatures between 15 to 25 degrees Celsius (59 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit). Furthermore, quinoa cultivation is versatile in terms of altitude, having an optimum range of 2,500 to 4,000 meters (8,200 to 13,100 feet) above sea level. It prefers well-drained soil with a pH range of 6 to 7.5, necessitating a considerable amount of sunshine for robust growth.
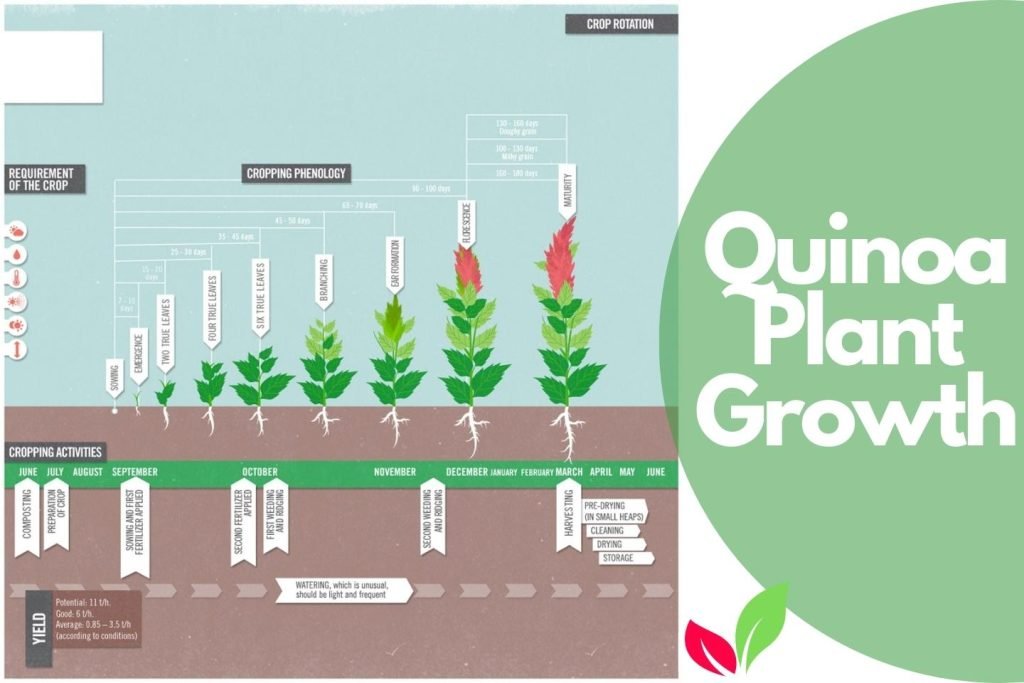
Quinoa Cultivation Process
Before embarking on quinoa cultivation, it is crucial to select high-quality seeds. Look for certified seeds from reputable sources to ensure the best results. Before planting, prepare the soil by conducting soil tests to determine its nutrient composition. Based on the results, enrich the soil with organic matter and necessary amendments to create an optimal environment for quinoa plant growth.
Planting and Germination
Quinoa can be planted through direct seeding or transplanting seedlings. Maintain a spacing of 30 to 40 centimeters (12 to 16 inches) between plants to provide ample room for growth. Germination typically occurs within 7 to 14 days, with soil temperatures between 15 and 20 degrees Celsius (59 to 68 degrees Fahrenheit) ideal for this stage. Maintain consistent soil moisture during germination to ensure successful sprouting.
Crop Care and Maintenance
Irrigation: quinoa cultivation requires adequate moisture throughout its growth cycle. Implement a suitable irrigation system, ensuring the soil remains moist but not soggy. Regularly monitor soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation frequency accordingly.
Fertilization: quinoa cultivation benefits from balanced nutrition. Apply organic fertilizers or incorporate compost into the soil before planting. Provide additional nitrogen and potassium-based fertilizers during the growing season to support robust growth.
Weed and Pest Control: Weeds can compete with quinoa plants for nutrients and space. Implement weed control measures such as mulching, hand weeding, or organic herbicides. Monitor for pests such as aphids, flea beetles, or moths and apply organic pest control methods when necessary.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Processing
Quinoa is typically ready for harvest when the plant turns golden, and the seeds are firm. Harvesting methods include either hand harvesting or using mechanical equipment for large-scale production. After harvest, remove any remaining plant material and proceed with post-harvest processing, including cleaning, drying, and storing the quinoa seeds in a cool and dry place to maintain their quality.
Common Challenges and Solutions
During quinoa cultivation, several challenges may arise. Pests like aphids or diseases such as powdery mildew can affect crop health. Implement preventive measures such as crop rotation, proper spacing, and regular monitoring for early detection. If pest or disease infestation occurs, opt for organic and environmentally friendly solutions such as neem oil or companion planting.
Nutritional Benefits and Culinary Uses of Quinoa
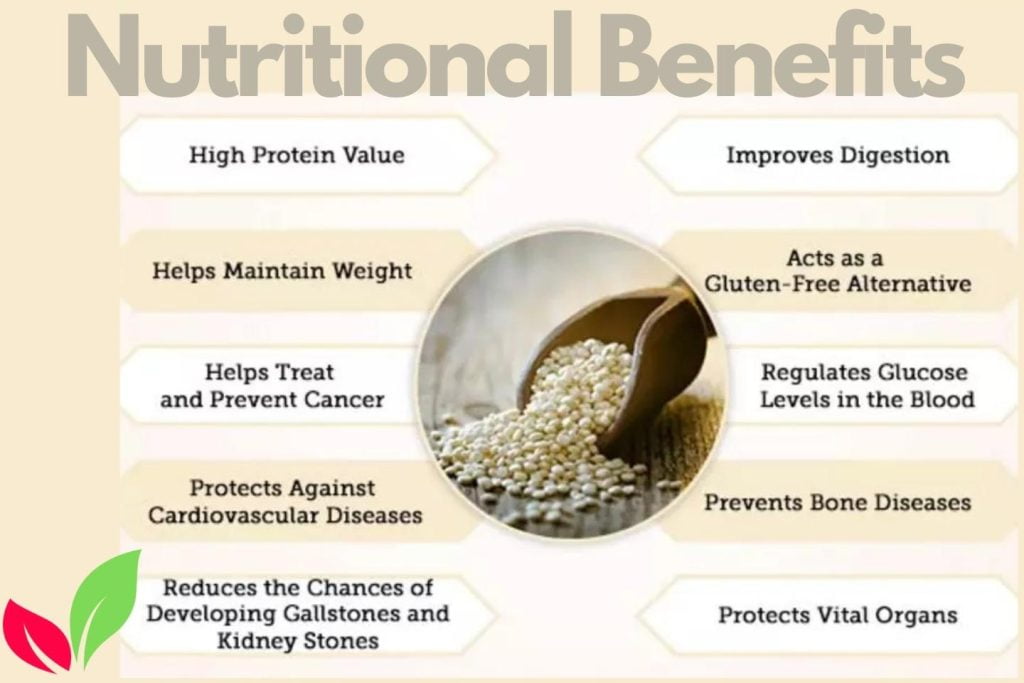
Quinoa’s unique nutritional profile makes it popular for health-conscious individuals, including college students. It is filled with complete proteins, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Quinoa provides ample support for a healthy digestive system. It promotes effective weight management and enhances overall well-being. Incorporate quinoa into your diet by exploring various culinary options, including salads, stir-fries, grain bowls, and baked goods. Experiment with different recipes to enjoy the diverse flavors and textures of quinoa.
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) – Quinoa, uncooked | Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) – Quinoa, cooked |
|---|---|
| Energy 1,539 kJ (368 kcal) Carbohydrates 64.2 g Dietary fibre 7.0 g Fat 6.1 g Monounsaturated 1.6 g Polyunsaturated 3.3 g Protein 14.1 g Vitamins Quantity%DV† Vitamin A equiv. 0%1 μg Thiamine (B1) 31%0.36 mg Riboflavin (B2) 27%0.32 mg Niacin (B3) 10%1.52 mg Vitamin B6 38%0.49 mg Folate (B9) 46%184 μg Choline 14%70 mg Vitamin C 0%0 mg Vitamin E 16%2.4 mg Minerals Quantity%DV† Calcium 5%47 mg Copper 30%0.590 mg Iron 35%4.6 mg Magnesium 55%197 mg Manganese 95%2.0 mg Phosphorus 65%457 mg Potassium 12%563 mg Sodium 0%5 mg Zinc 33%3.1 mg Water 13.3 g | Energy 503 kJ (120 kcal) Carbohydrates 21.3 g Dietary fibre 2.8 g Fat 1.92 g Monounsaturated 0.529 g Polyunsaturated 1.078 g Protein 4.4 g Vitamins Quantity%DV† Vitamin A equiv. 0%0 μg Thiamine (B1) 9%0.107 mg Riboflavin (B2) 9%0.11 mg Niacin (B3) 3%0.412 mg Vitamin B6 9%0.123 mg Folate (B9) 11%42 μg Choline 5%23 mg Vitamin C 0%0 mg Vitamin E 4%0.63 mg Minerals Quantity%DV† Calcium 2%17 mg Copper 10%0.192 mg Iron 11%1.49 mg Magnesium 18%64 mg Manganese 30%0.631 mg Phosphorus 22%152 mg Potassium 4%172 mg Sodium 0%7 mg Zinc 11%1.09 mg Water 72 g |

Is Quinoa Good For You?
Yes, quinoa is considered highly nutritious and beneficial for overall health. Here are some reasons why quinoa is good for you:
- Quinoa is nutrient-dense: A complete protein, it contains all nine necessary amino acids. Quinoa contains antioxidants, B vitamins, minerals, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and dietary fiber. These nutrients boost energy, immunological function, and cell repair.
- Gluten-Free: Quinoa is naturally gluten-free, making it a good alternative for celiacs. It’s gluten-free and healthy.
- Quinoa is rich in fiber: Fiber assists digestion, satiety, and blood sugar regulation. Quinoa in a balanced diet helps digestion and general health.
- Balanced Macronutrients: Quinoa contains carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Quinoa’s complex carbs and proteins boost energy and satiety.
- Low Glycemic Index: Quinoa raises blood sugar slowly, unlike high-glycemic meals. People with diabetes and weight watchers can benefit from this trait.
- Quinoa can be used in many different dishes. It can replace rice or pasta in salads, stir-fries, grain bowls, soups, and more. Its mild, nutty flavor goes well with many spices and seasonings.
Incorporating Quinoa into your diet can boost overall health and provide nutrient-dense benefits. It is a versatile and gluten-free option for individuals seeking a nutritious and balanced eating pattern.

Cooking Quinoa
Quinoa cooking instructions:
- Rinse quinoa before cooking to remove bitter or soapy residue. Rinse quinoa in a fine-mesh strainer under cold water while gently massaging it.
- Quinoa and liquid, 1.5 to 2 cups per cup of quinoa. Vegetable broth or stock can flavor water. Your serving size determines the amounts.
Stovetop cooking:
- Combine washed quinoa and measured liquid in a medium saucepan.
- Boil it.
- After it boils, lower the heat, cover the saucepan, and simmer for 15-20 minutes until the quinoa is soft and the liquid is absorbed.
- Let the quinoa simmer and fluff for 5 minutes after cooking.
- Finally, fork-fluff the quinoa before serving.
Rice Cooker:
- Rinse and measure.
- Add rinsed quinoa and measured liquid to the rice cooker.
- Close the rice cooker and choose the grain or white rice setting.
- After the cooking cycle, fluff the quinoa with a fork.
- Note: Quinoa varieties and personal preferences affect cooking times. Adjust cooking time for desired tenderness.
Cooked quinoa can be used in grain bowls, salads, soups, stews, and baking. It’s airy and slightly nutty. To flavor quinoa recipes, add herbs, spices, and other seasonings.

Conclusion
Quinoa cultivation provides an exciting opportunity for college students interested in sustainable farming practices and incorporating nutrient-rich foods into their diets. By following this comprehensive guide, you can confidently embark on your quinoa cultivation journey. Embrace the satisfaction of growing your quinoa crops while reaping the nutritional benefits and enjoying this exceptional grain’s culinary versatility. Start cultivating quinoa today and nourish both bodies and mind with this incredible superfood.




